Business information is tricky to handle if you aren’t intentional with it.
That’s where information governance helps you protect and utilize information to its full potential.
In this article we’ll cover:
- The definition of information governance,
- How to create an information governance framework,
- The role of email archiving in information governance and
- 4 best practices.
What Is Information Governance?
Information governance (IG) is the process of developing a defined decision and accountability framework that ensures proper actions are taken regarding the creation, use, storage, and access of information.
It encompasses policies, processes, frameworks, and controls that guide the effective use of structured and unstructured data in an organization.
- Policies define how information should be managed within an organization. They cover aspects such as data classification, data retention, and data privacy.
- Processes are the workflows and procedures put in place to implement the policies.
- Controls are the mechanisms that are used to enforce the policies and processes. They can include access controls, encryption, and audit trails.
- Frameworks provide a structured approach to implementing information governance within an organization.
The goal of information governance is to ensure data assets are available to those who need them while streamlining data management, reducing costs, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Implementing information governance processes in your organization is important for achieving your goals regarding proper data usage.
Why Is Information Governance Important?
Information governance makes your organization work more efficiently by allowing those who need specific information to get access to it more quickly.
A good information governance strategy allows you to work in line with regulations and eliminate potential costs and legal measures against your business due to missteps in managing your information.
It essentially balances the value and risk of each piece of information.
Especially with huge databases, information governance allows you to keep data up-to-date, making it both accurate and reliable for the user.
Establishing an information governance council made up of key stakeholders in the organization, including top-level management and IT personnel further helps the organization enforce governance policies.
Lastly, with the threat of data breaches, information governance (along with archiving) is key to keeping data protected from unauthorized access while complying with data retention and protection laws.
Organizations that implement information governance experience huge benefits:
- Meeting regulatory compliance requirements.
- Reducing ediscovery and litigation costs.
- Increase in operational and data transparency.
- Boost in staff productivity and efficiency.
- Improved data management.
The Information Governance Process
The information governance process is a comprehensive approach to managing and protecting your information assets that involves key steps to ensure their security and accuracy.
This process varies from organization to organization. However, it can be defined in five steps:
- Record management — Developing a comprehensive strategy for capturing, and managing records, including policies for creation, classification, retention, and disposal.
- Information rights — Creating and enforcing controls based on the principle of least privilege and ensuring only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information.
- Information security — Establishing a detailed data security policy that covers data protection, including encryption and intrusion detection systems.
- Email management — Creating policies for proper email usage, email archiving, and retention through the use of email archiving software.
- Audit — Conducting regular audits of implemented information governance processes and policies to assess compliance and identify areas for improvement.
Information Governance Frameworks
With each organization having its set of goals and objectives along with process frameworks gives us a clearly defined structure on how we should handle our information governance.
However, because of the differences in organizations, there isn’t one information governance framework that can conform to every organization.
To build your framework, first, you need to define the intricate details of how your organization utilizes data.
To do this, you can answer the following questions:
- What does information represent for my organization?
- Who uses this information?
- How is information created in my organization?
- Who can access which type of information?
- What is the information used for?
- How long is information useful to us?
- Which processes depend on my information?
Answering these questions for every information asset at your organization will give you the path to effectively managing them.
It all begins with a clear framework your organization needs to follow.
This information governance framework should be defined by its:
- Policy — Your framework should define which corporate policies and procedures are relevant to the information governance strategy. This includes your data security, record management, data retention, and disposal policies.
- Processes — The framework needs to define how information governance policies are implemented and utilized within each time frame (daily, monthly, annually).
- Metrics — You need to track information quality, access, and its lifecycle by establishing quality metrics and measuring these activities.
- Data management — The framework should define how employees manage specific data including legal and regulatory compliance, acceptable data types, and how this data is managed, stored, and archived.
- Roles — Proper information governance roles need to be defined in each stage of the data lifecycle including every employee’s responsibility by which they should be accounted.
- Disaster recovery — The framework should clearly outline company procedures in the event of a data breach, including how to report information losses and breaches, incident management specifics, and recovery processes.
- Monitoring — A clear monitoring plan should detail how information access and use are monitored.
Why Information Governance Is Important For Email Management
Recent years have brought the rapid and progressive growth of email traffic, putting pressure on companies to handle their email communication and storage space with much more care.
Facing problems with inbox overload, regulatory compliance, and lack of storage space, most companies do a poor job of maintaining their email integrity and efficiency and continue using email servers as storage solutions.
However, an obvious and major downside to this approach is that it clogs your email servers.
Piling up of emails, poor folder hierarchies and the absence of a systematic approach to email organization lead to the degradation of mail servers, which were never intended to act as storage repositories for vast amounts of email.
On the other hand, all business-critical data, especially email, must be readily available at all times, even in extreme cases of downtime and server failure. So what do you do?
Email governance requirements
Given the importance of email archiving, many industries set special rules on how their emails need to be managed.
These requirements include the following:
- The email archiving system needs to preserve the content and structure of emails.
- The system needs to be able to protect emails from unauthorized loss and destruction.
- The system you use to manage emails must ensure all your emails are discoverable, retrievable, and usable for the period specified in their retention schedule.
- The staff needs to know how to differentiate between permanent, temporary, transitory, and non-record email messages.
- The staff needs to know how to handle emails that contain classified national security information.
How Email Archiving Achieves Information Governance
Information security and archiving technology are crucial pieces in the governance puzzle.
Information availability and protection are two seemingly opposite, even conflicting organizational notions, and it’s one of the goals of information governance to unite and create a balance between the two.
Email archiving is the key to keeping your data safe and well organized while making it available to the personnel who request it.
Think of email archiving as your central repository for all of your organization’s communications information.
To be prepared for litigation and stay in compliance with various state and industry regulations, companies need to ensure that all enterprise data is accurate, authentic, available, and protected.
It is an automated process in which all incoming, outgoing, and internal email traffic is tracked, captured, retained, and protected so that the messages can be accessed at a later date if necessary.
Solutions like Jatheon are equipped with advanced features allowing you to govern all of your information without the need for multiple solutions.
It keeps all of your data in a separate cloud-storage server making room on your email server while protecting it from data breaches with advanced encryption protocols.
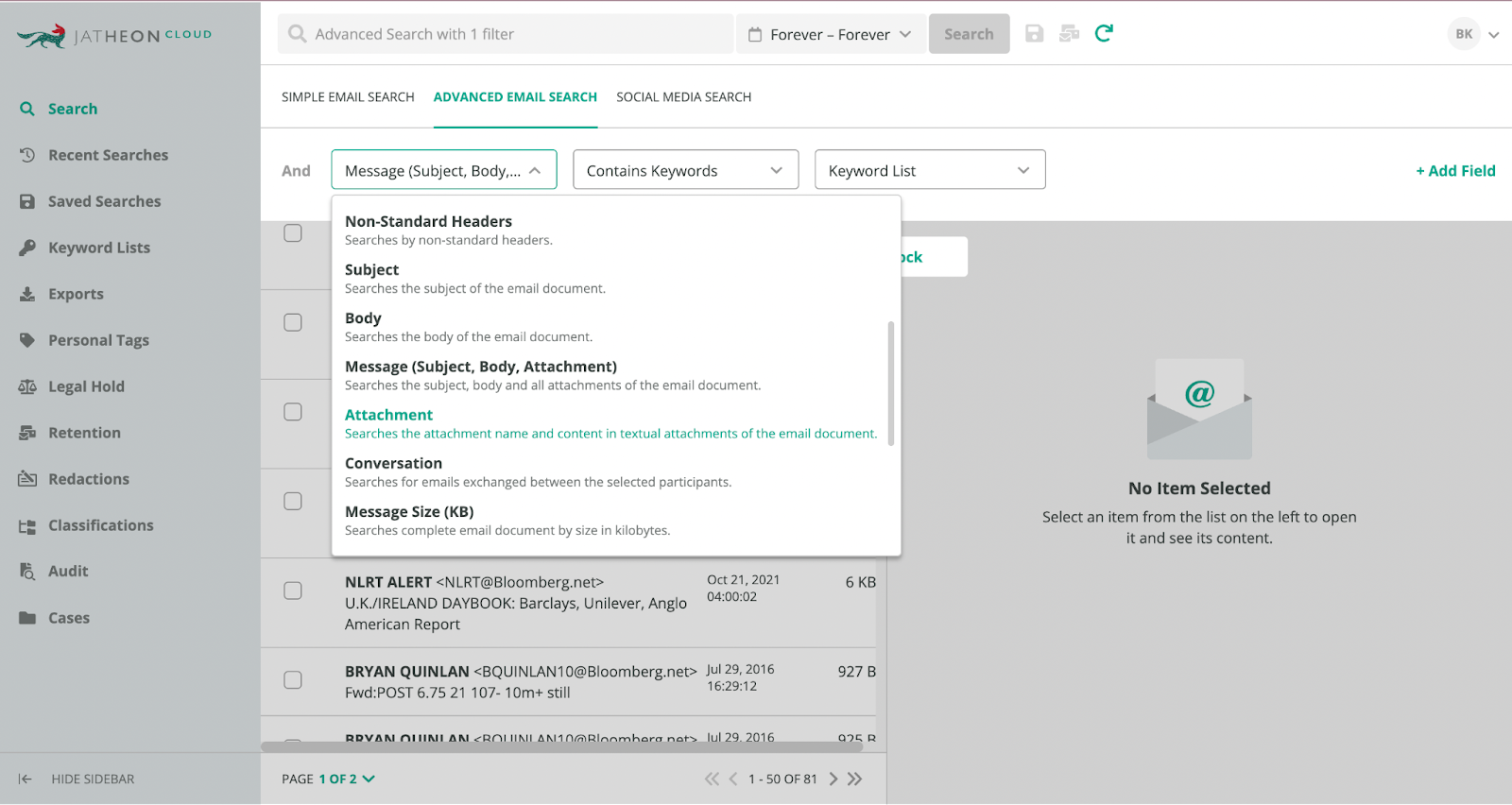
All the captured information is indexed and written in a WORM format with the ability to easily find it using advanced filtering options like keyword, fuzzy, proximity, and boolean searches.
With the importance of information in litigation cases, this ediscovery aspect is invaluable for any email archiving solution.
The archive also gives responsible personnel an easy way to grant or revoke any permissions, perform audit checks, and monitor the whole archive for potential information misuse.
Basically, in the modern era, email information governance can’t exist without email archiving.
Email Information Governance Best Practices to Implement
Now that you know the importance of information governance, here are our five steps to better information governance:
Mapping
Think about all the email information your organization produces and receives.
Ask yourself:
- Do I know where everything is stored?
- Is there a backup for all of my data?
- Do I know who’s in charge of which information?
The rate at which new information is being created is skyrocketing, with 90% of all the data in the world being generated over the last two years.
Now think about email data, most of it is unstructured textual data we use for business, however, this data also includes email attachments, social media content, voicemails, text messages…
This information is typically scattered across various servers, PST files, and your entire organization, which makes it very difficult to control and use proactively.
In addition, employees often create, access and manage business information from personal devices.
To contain this vast amount of information, you first need to create a data map and identify the types of data in your organization, including the legacy content that’s stored in old systems.
Data archiving solutions also help you archive all of this data in a single, central place. Just imagine email, social media, Zoom calls — all in a single repository.
This makes it easy for you to manage and find data quickly.
Encryption
The cornerstone of all information governance is its safety, both internal and external.
After creating your policies and assigning roles in your organization, your information should undergo another level of protection.
Encryption allows you to protect all of your data from unauthorized access and significantly decreases the chances of data breaches.
Most email archiving solutions utilize industry-standard encryption protocols to protect sensitive business information.
Evaluation and discovery
Having created a data inventory and documented the types of data in your enterprise, you should evaluate your current email management practices and identify room for improvement.
Analyze your enterprise information, delete duplicates, clean old files, and devise a plan on how to mitigate the exposure of private, protected, or sensitive information.
Make sure you identify and document the exact locations of all unstructured data, and don’t forget to include external hard drives, personal computers, and mobile devices.
Improve your policy
To stay on top of your enterprise information throughout its lifecycle, you’ll need to preach and revise your policy continuously.
In other words, you need to understand governance as an ongoing project, be dedicated to monitoring and improving your policies and procedures regularly, and stay up-to-date with regulations.
Finally, a good, holistic archiving solution will also allow you to leverage these enormous amounts of archived information through content analytics.
This lets you extract business value from the data you store, help you learn about your organization, and detect potential problems before they escalate.
Conclusion
Let’s recap the most important points:
- Information governance is the process of defining processes regarding information creation, storage, and use.
- It allows you to work in line with regulations while effectively managing your information.
- The information governance frameworks include creating policies, processes, metrics, and roles, and implementing data management and monitoring.
- With the abundance of information in email inboxes, email governance is imperative to an organization’s information governance.
- Email archiving allows you to store, manage, and make information available throughout your organization enabling its governance.
Stay compliant with major data retention laws with Jatheon’s archiving solution. Capture data automatically, find important information, and manage your data with ease.
Read Next:Data Inventory and Data Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide What Is Data Archiving? Definition, Benefits, and Best Practices |