While Microsoft Exchange and Outlook might seem interchangeable at first glance, these two cornerstones of Microsoft’s email ecosystem serve distinct purposes. It’s understandable why many find them confusing — both handle email, calendars, and contacts — but their differences become clear upon closer examination.
Let’s examine the key distinctions between these services and uncover why the conversation isn’t so much about Microsoft Exchange vs. Outlook but rather how they complement each other.
Here’s what you’ll find out in this article:
- What is Microsoft Exchange
- What is Microsoft Outlook
- Do these two services have the same purpose
- What are the differences between Microsoft Exchange vs. Outlook
- How to choose which one will work best for your needs
TL;DR: What’s the Difference Between Microsoft Exchange and Outlook?
Both Exchange and Outlook are essential to Microsoft’s email ecosystem. Exchange acts as the server infrastructure, handling organizational email communication and data storage. Outlook, on the other hand, is a user-facing client application providing tools to access and manage emails, calendars, and contacts. Simply put, Exchange manages the backend, while Outlook is the user interface.
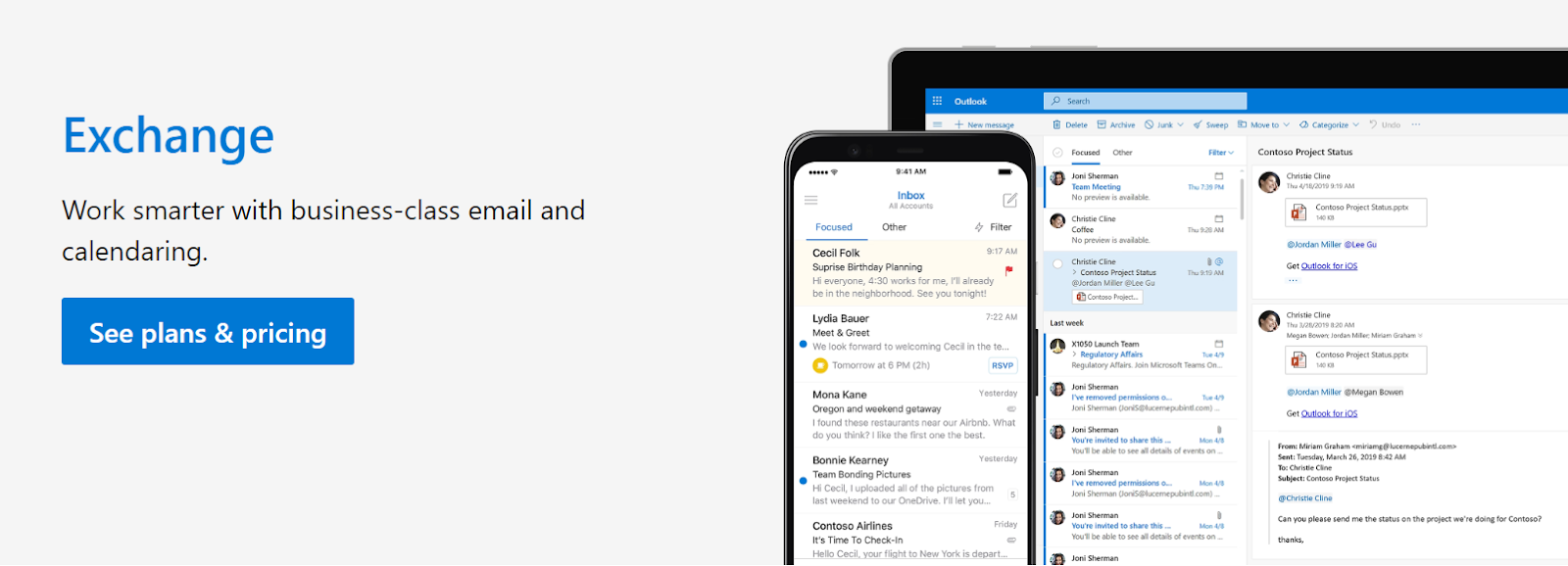
What Is Microsoft Exchange?
Microsoft Exchange is a mailing and calendaring server that enables digital communication and collaboration within a business. Exchange service implies a specialized network resource management application that communicates with email clients using transmission control protocols, including IMAP, SMTP, and POP.
Source: Microsoft
To put it another way, Microsoft Exchange is in charge of sending and receiving emails from and to client computers. Although Exchange may be used with any email client, it is most typically used with Microsoft Outlook.
Exchange is a part of Microsoft Office 365 Business Plans and Enterprise plans, the company’s productivity and collaboration suite. The price tag of Microsoft Exchange starts from $4/month per user and goes up to $12.5/month per user for their whole suite of products.
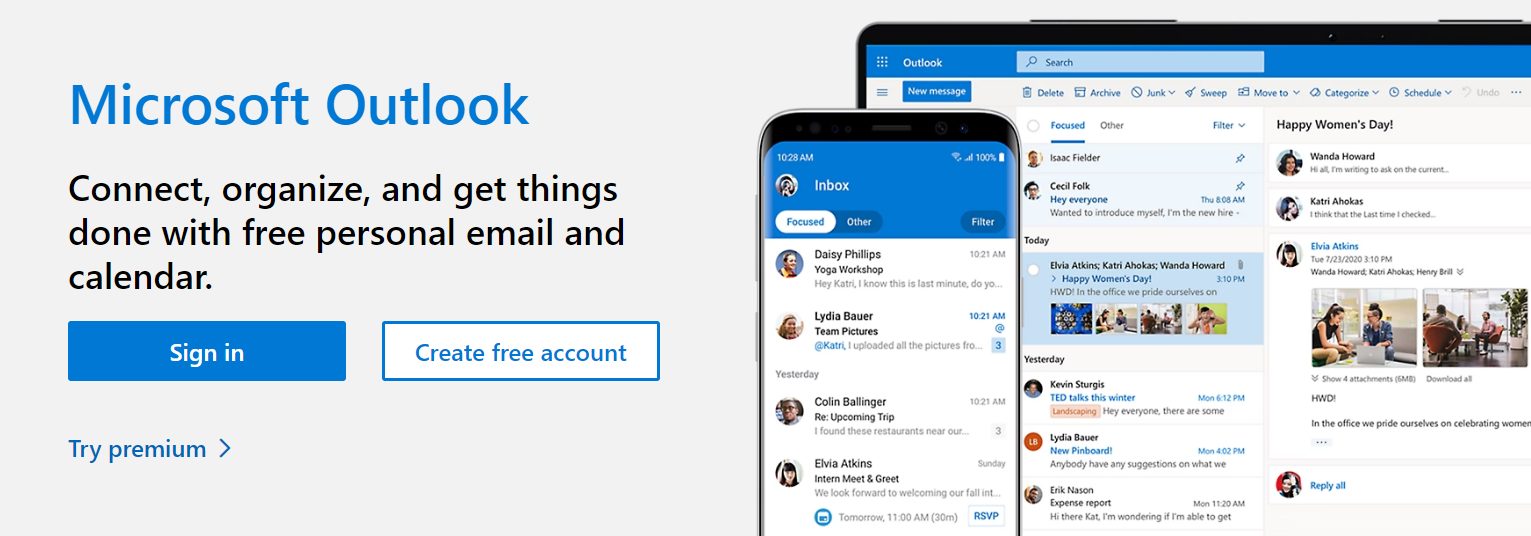
What Is Microsoft Outlook?
Microsoft Outlook is a mailing and calendaring app that is part of the Microsoft Office 365 suite. It is mainly used for email but also allows users to manage contacts, tasks, calendars, and more in one place.
Source: Microsoft
Outlook is an email client — a simple application that you install on your computer that allows you to send and receive emails via protocols to and from an email server.
You can use Outlook without a connection to the Microsoft Exchange Server. While this limits access to collaborative features like shared calendars and contacts, classic Outlook for Windows still supports connections to other email services using IMAP and POP3 protocols, allowing access to services like Gmail, Yahoo, and custom email providers.
However, the new Outlook for Windows (replacing the Mail and Calendar apps) does not support POP3 as of early 2024, although Microsoft plans to roll out POP support gradually. Also, Outlook.com no longer allows linking third-party email accounts via the Connected Accounts feature as of July 1, 2024.
You can use Outlook without connecting to Exchange, but you’ll have to work offline, which means you’ll lose access to email and other collaborative features.
Is Microsoft Exchange the Same As Outlook?
While both handle your emails, calendars, and contacts, Microsoft Exchange and Outlook serve distinct functions. Exchange operates as a robust server infrastructure, while Outlook provides a user-friendly interface for accessing and managing your information.
In other words, they are interconnected components of Microsoft’s mailing and communication service that work on different levels of implementation.
Think of Microsoft Exchange as the backbone of the business’s communication system, providing a server software that handles all email communications, calendaring, and collaboration within a business.
On the other hand, Microsoft Outlook is the client application that end users interact with to access their emails, calendars, and contacts. It is somewhat like a user interface that connects the user with Exchange in the background.
One provides the services (Exchange), while the other gives users the ability to access and use those services (Outlook). They work together to provide a comprehensive communication solution.
Now that you understand what each solution does, let’s take a look at which one is right for you.
Microsoft Exchange vs. Outlook
For a clearer understanding, here’s a concise comparison between Microsoft Exchange and Outlook:
| Microsoft Exchange | Microsoft Outlook |
| Microsoft Exchange is a server application and an email server solution. This means that Exchange is a dedicated network resource management platform. | Outlook is an email client installed on your desktop. Outlook is designed to send and receive emails, and it keeps in sync with Exchange. |
| Exchange is offered as a part of Microsoft 365 Business, Enterprise, and Office 365 Enterprise plans, or purchased separately. | Microsoft Outlook is included in the Microsoft Office suite. It’s a part of all versions of Office 365 for business |
| Exchange can be used both with Outlook and other email clients. | Outlook can’t be used with email servers other than Exchange. It’s possible to use it without Exchange, but it requires working offline. |
| Exchange is usually accessed by IT administrators and database operators. | Outlook is accessed by end-users for day-to-day email communication. |
Beyond the basics, let’s explore some key differences you’ll notice when using Exchange and Outlook:
Collaboration and user management
While Outlook allows you to manage groups and collaborate, they are rather basic features compared to Exchange. Exchange provides extensive options for collaboration and team structure. Admins have granular control over user and team permissions, as well as the ability to create and distribute resources, contacts, and subgroups.
UI and access
Unlike Exchange, Outlook offers a user-friendly interface with a clean and professional design available both on desktop and mobile devices. This makes it easy for users to discover what they are searching for.
On the other hand, the Exchange admin interface might be substantially more intimidating, especially for new users. This dashboard provides you with the tools you need to manage your organization’s hosted email, but it may take some time to become acquainted with its features and possibilities.
Security
When it comes to security, Exchange outperforms Outlook at all levels. Unlike Outlook, which just filters spam emails into the Junk folder, Exchange security features are significantly more versatile. Admins can actively filter communications based on business policy or regulatory requirements to guarantee organization-wide compliance.
Message size limitations
Exchange allows users to send messages far larger than those enabled by Outlook. Individual messages in Outlook are limited to a total size of 20 MB, compared to 150 MB for Exchange users. However, keep in mind that huge files may be rejected by the recipient’s email client.
Key Considerations when Choosing a Hosting Service
While Microsoft Outlook and Exchange are popular choices, they’re just two options among many other email hosting services. Being backed by a tech giant doesn’t automatically make them the best fit for every organization.
In fact, it could make more sense for you to look into alternatives to Microsoft Exchange and Outlook alternatives.
Before you begin your search, you should familiarize yourself with the various email hosting alternatives accessible to you. There are three main types of email hosting:
- Self-hosting: You keep your emails on your own server.
- Shared hosting: You use a third-party supplier to bundle web and email hosting.
- Third-party hosting: You rent email storage space on the server of a third-party provider.
Once you’ve determined which email hosting model is best for your company, you’ll want to thoroughly examine providers based on a variety of criteria, including:
- How much do their services cost
- What features and functionality are available
- Whether or not they permit custom domains
- Whether or not they employ spam filters
- How much mailbox storage space do they offer
- What security protocols do they have in place
- How they intend to utilize your data and who will have access to it.
Microsoft Exchange and Outlook — A Powerful Synergy
From comparing these two solutions you might have noticed that they aren’t completely different and that you shouldn’t look at them as some kind of competitors.
Microsoft Exchange and Outlook are complementary solutions that work better together, and that’s what they were intended for — to be paired.
If you consider Microsoft’s communication suite as the best option for you, or you found another emailing solution there’s one more important detail you should think about — email archiving.
Jatheon provides you with the best cloud email archiving solution that will keep your business compliant and cater to your ediscovery needs.
Book a free live demo and secure your email data.
Summary of the Main Points
- Microsoft Exchange and Outlook are complementary tools, not competitors. Exchange is a powerful server infrastructure that handles email, calendars, and business collaboration, while Outlook is the client that allows users to access and manage their Exchange data seamlessly from their desktops and mobile devices.
- Outlook has a user-friendly interface, while Exchange’s admin interface is more complex.
- Exchange comes with robust security features, while Outlook primarily focuses on spam filtering.
- Exchange allows for larger message sizes than Outlook, making it more suitable for business users.
- Outlook, in combination with any email service, can fulfill the needs of individual users and small businesses.
- Larger organizations with advanced collaboration requirements should opt for Exchange with Outlook as the client.
FAQ
Should I use Outlook or Exchange email?
This depends on your specific needs and context. Individual users and small businesses can use Outlook as their email client (it can connect to various email services, including Exchange). For larger organizations and those that need advanced collaboration features, Microsoft Exchange plus Outlook as the client to access Exchange services can be the right choice.
Is Hotmail now Outlook or Exchange?
Hotmail was officially discontinued in 2013 and is now Outlook. You may still come across hotmail.com email addresses, as some users decided to keep them when Outlook took over.
Is Exchange part of Office 365?
Yes, Exchange Online is the email and calendaring component of Microsoft 365 and Office 365. Microsoft Exchange Online is a cloud-based version of the traditional Exchange server. It provides email hosting, calendar management, contacts, and other essential collaborative features for businesses and organizations.
Do I need Exchange with Office 365?
No, you don’t need a separate Exchange license to send, receive, or manage mail from your Microsoft 365 account. Microsoft 365 provides various plans with different features, and the email and calendaring services are provided through a component known as Exchange Online.
What is better than Outlook for email?
Google Workspace is a great alternative to Outlook because it offers shared drives and more storage space. Other Outlook alternatives for businesses include HLC Notes, Zimbra, and Microsoft 365. When choosing an alternative to Outlook for your organization, it’s important to consider factors like company size, integration and compatibility with your existing systems and tools, security requirements, and the learning curve for your team.
Can I use Outlook with my personal Gmail or Yahoo account?
Yes, you can use Microsoft Outlook with personal email accounts like Gmail or Yahoo. Specifically, Classic Outlook for Windows supports standard email protocols such as IMAP and POP3, which allow you to connect to various email providers. This makes Outlook a versatile tool for managing both personal and professional communications in one place. However, please be aware that the “new” Outlook for Windows implementation may have different capabilities.
What’s the difference between Classic Outlook for Windows and the “new” Outlook?
Classic Outlook for Windows is the traditional, feature-rich desktop application that has been used for many years. The “new” Outlook for Windows is a more streamlined application designed to replace the built-in Mail and Calendar apps in Windows. It’s intended to be more closely aligned with the web-based Outlook.com experience. Key differences currently involve feature sets, user interface, and protocol support, with the “new” Outlook undergoing ongoing development.
Read Next:10 Microsoft Outlook Alternatives to Try in 2024 |